PCB Assembly Services
Through Hole PCB Assembly
JHYPCB offers end-to-end through-hole PCB assembly (THT Assembly) from prototypes to production.
At JHYPCB, we offer end-to-end through-hole PCB assembly (THT Assembly) from prototypes to production. We are committed to the delivery of high-end technology solutions. To this end, we offer a complete range of through-hole PCB assembly capabilities resulting in PCBs that are in compliance with international quality standards.
Our through-hole PCB Assembly services comprise of both manual and automated techniques. While our manual techniques can handle complex assemblies, the automated ones are best suited for small-volume production as also reduced material handling. We provide through-hole PCB assembly at the highest quality level and in a cost-effective manner.
What is Through Hole PCB Assembly Service?
Through-hole PCB Assembly Service refers to the process of assembling electronic components onto printed circuit boards using through-hole technology. Through-hole technology involves drilling holes into the PCB and then inserting the leads of the electronic components into these holes. The components are then soldered in place on both sides of the board to create a reliable electrical connection.
Through-hole PCB Assembly Service is commonly used in the manufacturing of high-reliability electronic products, such as aerospace, medical, military, and industrial equipment. The process is also used for prototyping, small-batch production, and for components that require high mechanical strength or high-power handling.
Through-hole PCB Assembly Service typically includes a range of processes, including PCB fabrication, component insertion, wave soldering, manual soldering, and testing. The service provider will work closely with the customer to ensure that the design and assembly processes meet the specific requirements of the application and that the final product is of the highest quality and reliability.

The features and benefits of the through-hole PCB assembly
Through-hole PCB Assembly offers several features and benefits, including:
Strong mechanical stability: Through-hole technology provides a stronger mechanical bond between components and the PCB, making it ideal for applications that require high vibration or mechanical stress.
High power handling: Through-hole components can handle higher levels of electrical power, making them well-suited for applications that require high-current or high-power devices.
High-reliability: Through-hole components provide a more reliable connection due to the strong mechanical bond and less sensitivity to environmental factors such as temperature and humidity.
Wide range of components: Through-hole technology supports a wider range of electronic components than surface mount technology, including large components such as capacitors and transformers.
Simple and easy to repair: Through-hole components are easier to replace and repair than surface mount components, making the repair process simpler and less time-consuming.
Better thermal management: Through-hole components provide better thermal management due to their larger size and stronger mechanical bond, which helps to dissipate heat more efficiently.
Compatibility with lead-free soldering: Through-hole components are compatible with lead-free soldering, making it easier to meet environmental regulations and reduce the environmental impact of electronic products.
Overall, through-hole PCB assembly offers a range of features and benefits that make it a popular choice for high-reliability electronic products, especially those that require high mechanical strength, high power handling, and a wide range of components.
Composition of through-hole PCB assembly
Through-hole PCB Assembly typically consists of the following components:
Printed Circuit Board: This is the base material that provides the physical support and electrical connections for the components. The PCB is typically made of a non-conductive material, such as fiberglass or plastic, with conductive traces and holes drilled into it to allow for the insertion of through-hole components.
Through-hole Components: These are the electronic components that are inserted into the holes on the PCB and soldered in place to create a reliable electrical connection. Through-hole components include resistors, capacitors, diodes, transistors, and other electronic devices.
Solder: Solder is a metal alloy that is melted and used to create a permanent electrical and mechanical connection between the through-hole component and the PCB. The solder is typically applied using wave soldering or manual soldering techniques.
Flux: Flux is a chemical substance that is used to clean and prepare the surface of the through-hole component and the PCB before soldering. The flux helps to remove any oxides or impurities from the surfaces, making it easier for the solder to create a strong bond.
Solder Paste: Solder paste is a mixture of metal particles and flux that is used in the surface mount technology (SMT) process. However, in some cases, it may also be used in through-hole PCB Assembly to facilitate the insertion of certain components.
Testing and Quality Control: Once the through-hole PCB Assembly is complete, it undergoes testing and quality control procedures to ensure that it meets the required specifications and standards. This may include functional testing, electrical testing, visual inspection, and other quality control measures.
Assembly Equipment: Through-hole PCB Assembly requires specialized equipment to insert and solder the through-hole components onto the PCB. This includes through-hole insertion machines, wave soldering machines, and manual soldering stations.
Design Files: The through-hole PCB Assembly process requires design files that include the PCB layout and component placement information. The design files are used to create the PCB and to ensure that the components are correctly placed and soldered in place.
Work Instructions: Work instructions provide step-by-step instructions for the assembly process, including the placement and soldering of the through-hole components. Work instructions ensure that the assembly process is consistent and that the final product meets the required standards and specifications.
Documentation: Through-hole PCB Assembly requires documentation of the assembly process, including work instructions, quality control records, and other documentation to ensure that the final product meets the required standards and regulations. Documentation is essential for traceability and accountability in the manufacturing process.
Through-hole PCB Assembly Manufacturing Process
The Through-hole PCB Assembly manufacturing process typically involves the following steps:
PCB Fabrication: The first step is to fabricate the printed circuit board according to the design files, which includes drilling holes for the through-hole components.
Component Preparation: Through-hole components are prepared by cutting the leads to the appropriate length and cleaning the component leads with solvents or other cleaning agents.
Insertion: Through-hole components are then inserted into the holes on the PCB by hand or with automated insertion machines.
Soldering: Once the components are in place, the PCB is sent through a wave soldering machine or manually soldered to create a permanent electrical and mechanical connection between the component leads and the PCB.
Cleaning: The PCB is then cleaned to remove any flux residue or other contaminants that may have accumulated during the soldering process.
Inspection: The PCB is inspected to ensure that all components are correctly placed and soldered in place, and that there are no defects or other issues that would impact the functionality or reliability of the final product.
Testing: The final step is to test the PCB to ensure that it meets the required specifications and standards. This may include functional testing, electrical testing, and other quality control measures to ensure that the final product is reliable and performs as expected.
Throughout the manufacturing process, documentation is maintained to ensure traceability and accountability, including work instructions, quality control records, and other documentation to ensure that the final product meets the required standards and regulations.
Applications of through hole PCB assembly
Through-hole PCB Assembly has a wide range of applications in various industries, including:
Automotive: Through-hole PCB Assembly is used in the production of automotive electronics, including engine control modules, sensors, and other electronic systems.
Aerospace: Through-hole PCB Assembly is used in the production of aerospace electronics, including flight control systems, navigation systems, and communication systems.
Industrial Control: Through-hole PCB Assembly is used in the production of industrial control electronics, including motor control systems, power distribution systems, and process control systems.
Medical Devices: Through-hole PCB Assembly is used in the production of medical devices, including monitoring systems, imaging systems, and other medical electronics.
Telecommunications: Through-hole PCB Assembly is used in the production of telecommunications equipment, including routers, switches, and other network infrastructure devices.
Defense and Military: Through-hole PCB Assembly is used in the production of military electronics, including communication systems, radar systems, and other defense equipment.
Consumer Electronics: Through-hole PCB Assembly is used in the production of various consumer electronics, including home appliances, entertainment systems, and gaming consoles.
Through-hole PCB Assembly is preferred over surface mount technology (SMT) for applications that require high power or high-frequency components. The through-hole components offer better heat dissipation and mechanical stability compared to SMT components. The robustness of through-hole components makes them well-suited for harsh environments, such as aerospace and defense applications.
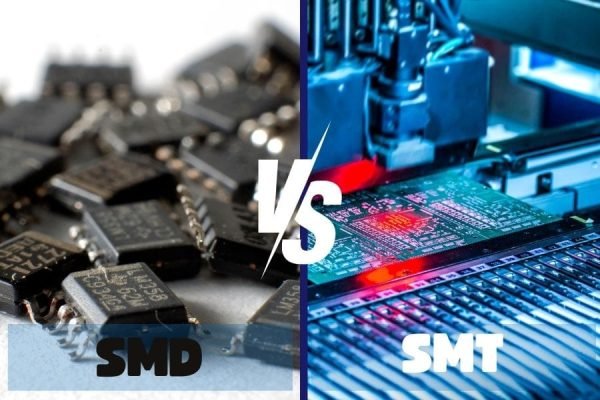
Comparison between Through-hole and Surface-mount Technology
Through-hole PCB assembly and Surface-mount Technology are two primary methods used in assembling electronic components on printed circuit boards.
Through-hole PCB Assembly: This method involves drilling holes through the board and then placing components in the holes, with their leads bent and soldered to the other side of the board. This method was widely used in the past but has now been largely replaced by SMT technology. It is still used in certain situations, such as when large components need to be securely mounted or when high-current components are used. Through-hole assembly is more suitable for prototyping and small-scale production.
Surface-mount Technology: SMT is a newer method of PCB assembly that does not require holes in the board. Instead, the components are placed directly onto the surface of the board and held in place with solder. This method allows for a greater number of components to be placed on the board, as well as a smaller overall size. SMT technology is faster, cheaper, and more suitable for high-volume production. However, it requires special tools and equipment, and the components used are generally smaller and more fragile than those used in through-hole assembly.
| Criteria | Through-Hole PCB Assembly | Surface-Mount Technology |
|---|---|---|
| Component Compatibility | Compatible with through-hole components | Compatible with surface-mount components |
| Component Size | Can accommodate larger components | Suitable for smaller components |
| High Power Capability | Offers better heat dissipation and can handle high power components | Limited power handling capability |
| Mechanical Stability | Provides mechanical stability to the PCB | SMT components are more fragile and require additional support |
| Ease of Replacement | Easy to replace components | Difficult to replace components |
| Customization | Can be customized to meet specific requirements | Limited customization options |
| Reliability | Offers high reliability and better resistance to mechanical stress | Lower reliability and more prone to failure |
| Cost-effectiveness | Cost-effective for low to medium volume production runs | More cost-effective for high volume production runs |
Overall, Through-Hole PCB Assembly and Surface-Mount Technology each have their advantages and disadvantages, and the choice between the two technologies depends on the specific requirements of the application. Through-Hole PCB Assembly is preferred for applications that require high power handling capability, mechanical stability, and ease of component replacement, while SMT is suitable for applications that require smaller components and high-volume production runs.
Capabilities of our through hole PCB assembly
We are fully equipped to handle the following through-hole PCB assembly services:
- Manual and automated placement of components
- Hand soldering
- Prototype build to high-volume assembly
- Double Wave Flow Solder
- RoHS soldering using tin-lead solder
- Selective Soldering
- Full range of Testing services: Functional testing, In-Circuit Testing, Automated Optical Inspection, X-Ray Inspection, Burn-in Tests
- Support various types of PCBs, including metal core PCBs, Rigid PCBs, Flex-rigid PCBs, FR4 PCBs, etc.
Above everything, we have a highly trained and experienced team that specializes both in hand soldering of components as also automated insertion for both axial and radial components as also automated dual wave solder.
In addition to through-hole PCB assembly, we also provide value-added services, such as conformal coating, labeling, surface finishing, and complete PCB encapsulation.