FR-4 PCB Fabrication Service
FR-4 Material Guide For PCB Fabrication
You can rely on our manufacturing expertise if you need quality FR4 PCB products. We have been supplying our partners and other original equipment manufacturers (OEM) with highly reliable and quick turn FR-4 PCB manufacturing service for many years.
Table of Contents
What is FR-4?
FR-4 is a type of composite material commonly used as a substrate in printed circuit boards. The term “FR-4” refers to the specific grade of the material, which is a flame-retardant type of glass-reinforced epoxy laminate.
- The “FR” in FR-4 stands for “flame retardant.” This means that the material is designed to resist burning or catching fire, which is an important safety feature in electronics. When exposed to flame, the material will not sustain combustion or will only burn with a self-extinguishing flame.
- The “4” in FR-4 refers to the woven glass fabric layers that are impregnated with epoxy resin to make the composite material. The glass fabric provides strength and rigidity to the material, while the epoxy resin acts as a bonding agent to hold the layers together. The “4” indicates the thickness of the woven glass fabric in units of ounces per square foot, with 4 oz being a common thickness used in FR-4 laminates.
Origin and History of FR-4
FR-4 substrate material was first introduced in the 1950s by the NEMA (National Electrical Manufacturers Association) as a flame-resistant glass-reinforced laminate for electrical insulation applications. The early versions of FR-4 were made from woven glass cloth impregnated with phenolic resin. These materials were not flame-retardant enough for some applications and were also prone to delamination due to moisture absorption.
In the 1960s, epoxy resin was introduced as a new type of binder for glass cloth. This led to the developing of a new generation of FR-4 materials with improved flame resistance, thermal stability, and mechanical strength. The use of epoxy resins also allowed for the development of thinner laminates with higher layer counts, which enabled more complex circuit designs.
Today, FR-4 is the most widely used substrate material for printed circuit boards, accounting for over 90% of the market. Many manufacturers worldwide produce the material, and it is available in a wide range of thicknesses, copper foil weights, and dielectric constants to meet the diverse needs of the electronics industry. The continued development of FR-4 materials and processes has improved electronic device performance, reliability, and cost-effectiveness.
FR-4 Applications
FR-4 has a wide range of applications in the electronics industry, particularly in manufacturing PCBs. Its high-performance properties, including electrical insulation, mechanical strength, thermal stability, flame resistance, and chemical stability, make it an ideal substrate material for producing complex and reliable PCBs.
FR-4 is commonly used in applications that require high-density, high-speed, and high-reliability circuits. It is widely used in consumer electronics, such as smartphones, tablets, laptops, and televisions, as well as in industrial and automotive electronics, aerospace and defense systems, and medical devices.
In addition to PCBs, FR-4 is also used to manufacture other electronic components, such as batteries, LEDs, transformers, and switches. It can also be used as a reinforcing material for mechanical parts, such as strengthening the strength and durability of plastic parts.
Physical and Chemical Properties of Fr-4
FR-4 is a composite material that has both excellent physical and chemical properties.
- Composition of FR-4: FR-4 comprises epoxy resin and glass fiber cloth, as well as fillers, additives, and other components. The epoxy resin provides a strong and stable base for the material, while the glass fiber cloth provides strength and rigidity to the laminate structure.
- Physical properties of FR-4: FR-4 has excellent mechanical properties, including high strength, hardness, and heat resistance. It is also dimensionally stable, with low thermal expansion coefficients, and has good electrical insulation properties.
- Chemical properties of FR-4: FR-4 has excellent chemical stability and is resistant to most acids, bases, and organic solvents. It is also highly resistant to water absorption and can maintain its mechanical and electrical properties in high humidity environments. Additionally, FR-4 has good flame retardant properties, which makes it suitable for use in applications where fire safety is a concern.
FR-4 Technical Parameter Table
Below is a table listing some of the technical parameters for FR-4 PCB material:
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Dielectric constant (εr) | 4.2 – 4.8 |
| Dissipation factor (tan δ) | 0.015 – 0.035 |
| Thermal conductivity | 0.3 – 0.4 W/m*K |
| Water absorption | <0.10% |
| Glass transition temperature (Tg) | 130 – 180°C |
| Operating temperature range | -40 to 130°C |
| Flammability rating | UL 94V-0 |
| Copper peel strength | >1.0 N/mm |
| Surface resistivity | >10^12 Ω/sq |
Note: The specific technical parameters of FR-4 can vary depending on the manufacturer and the specific grade of the material.
PCB Substrate Type
There are several types of substrate materials used in the manufacture of PCBs, including:
- Aluminum: Aluminum-based substrates are lightweight, have good thermal conductivity, and are often used for LED and power applications. However, they are unsuitable for high-frequency applications due to their high dielectric loss.
- Metal core: Metal core substrates are similar to aluminum substrates but have a metal core layer for better heat dissipation. They are commonly used for power applications.
- Copper: Copper-based substrates are highly conductive and are often used in high-frequency and high-speed applications. However, they are expensive and have poor thermal conductivity.
- Rogers: A high-performance substrate material made from a ceramic-filled hydrocarbon polymer. It has excellent electrical properties and is commonly used in high-frequency applications.
- Polyimide (PI): PI substrates have excellent thermal stability and can withstand high temperatures up to 400°C. They are commonly used in aerospace and military applications. However, they are expensive and difficult to manufacture.
- FR-4: FR-4 is the most widely used substrate material for PCBs, made from woven fiberglass cloth and epoxy resin. It has good mechanical and electrical properties, is relatively inexpensive, and is suitable for various applications. FR-4 substrates are available in different grades and thicknesses, depending on the specific requirements of the PCB design.
The choice of substrate material depends on the specific requirements of the PCB design, including the application, frequency, thermal management, and cost. Factors to consider when selecting a substrate material include the dielectric constant, thermal conductivity, coefficient of thermal expansion, and glass transition temperature. It is important to select a substrate material that can provide the required electrical and mechanical performance while also meeting the cost constraints of the project.
FR-4 is a popular PCB substrate material for its low cost, good mechanical strength, and electrical performance. However, it has a relatively low thermal conductivity and may not be suitable for high-power applications. High-speed and high-frequency designs may also require specialized FR-4 materials with improved electrical properties.
Different Tg Value in FR-4 PCB
FR-4 is a popular substrate material used to manufacture printed circuit boards (PCBs). Several types of FR-4 materials are available, including standard/regular FR-4, mid Tg FR-4, and high Tg FR-4.
| Parameter | Standard/Normal FR-4 | Mid-Tg FR-4 | High-Tg FR-4 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tg (°C) | 130-140 | 150-170 | 170-200 |
| Thermal conductivity | 0.25-0.45 W/(m*K) | 0.30-0.50 W/(m*K) | 0.45-0.70 W/(m*K) |
| Coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE) | 13-18 ppm/°C | 9-12 ppm/°C | 6-8 ppm/°C |
| Water absorption | <0.2% | <0.1% | <0.1% |
| Dielectric constant (Dk) @ 1 MHz | 4.4-4.8 | 4.4-4.6 | 4.2-4.4 |
| Dissipation factor (Df) @ 1 MHz | 0.016-0.025 | 0.012-0.015 | 0.009-0.012 |
| Tensile strength | 340 MPa | 340 MPa | 340 MPa |
| Flexural strength | 500 MPa | 500 MPa | 500 MPa |
Compared to standard FR-4, mid Tg and high Tg FR-4 materials have higher glass transition temperatures, which make them more suitable for high-temperature applications. They also have lower thermal coefficients of expansion, which means they are less likely to warp or crack under temperature changes. In terms of electrical properties, all three types of FR-4 have similar dielectric constants and dissipation factors. However, high Tg FR-4 has a slightly lower dissipation factor, which means it is more suitable for high-frequency applications.
The choice of FR-4 material depends on the specific requirements of the PCB design, including the operating temperature, frequency, and cost. High Tg FR-4 is typically used in high-temperature applications, while mid Tg FR-4 may be suitable for general-purpose applications. Standard FR-4 is the most widely used and cost-effective option for low-temperature applications.
What is Fr-4 PCB Board?
FR-4 printed circuit boards are made by etching a conductive pattern onto a laminate material composed of layers of glass fiber cloth and epoxy resin. The epoxy resin is impregnated into the glass fiber cloth and cured to form a rigid and durable substrate. The cured FR-4 material provides excellent mechanical and electrical properties, making it suitable for a wide range of electronic applications.
FR-4 PCBs can be single-sided, double-sided, or multilayered, depending on the complexity of the circuit design. The FR-4 material is compatible with various manufacturing processes, including through-hole plating, surface mount technology, and reflow soldering.
One advantage of FR-4 PCBs is their low cost, making them a popular choice for consumer electronics and other cost-sensitive applications. However, the performance of FR-4 PCBs can be limited by their low glass transition temperature (Tg), which affects their ability to withstand high temperatures and thermal stress. To address this limitation, high-Tg FR-4 materials have been developed, which offer higher thermal stability and improved performance at elevated temperatures.
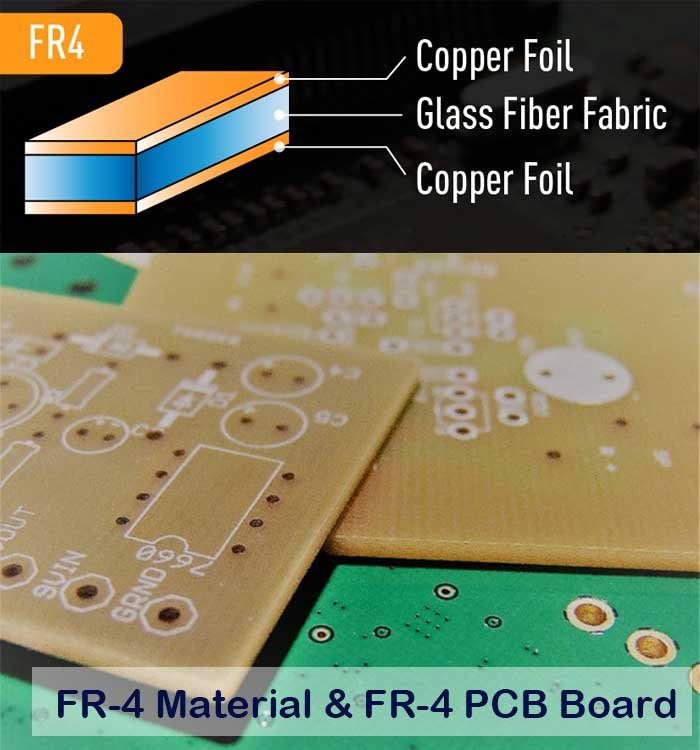
FR-4 PCB Thickness and How to Choose?
FR-4 PCB thickness is an important parameter to consider when designing and choosing PCBs. The thickness of FR-4 PCBs typically ranges from 0.2mm to 3.2mm, with 1.6mm being the most common thickness used in the industry.
Choosing the right thickness for an FR-4 PCB depends on a number of factors, including the desired mechanical strength, the size and weight of the components that will be mounted on the board, and the level of thermal management required.
Thinner FR-4 PCBs are often used in applications where space is limited or where weight is a concern, such as in mobile devices or small electronic products. Thicker FR-4 PCBs are often used in applications that require greater mechanical strength, such as in industrial control systems or automotive applications.
In general, it is recommended to choose an FR-4 PCB thickness that is appropriate for the specific application, taking into account the requirements for mechanical strength, component mounting, and thermal management. It is also important to consider the manufacturer’s capabilities and their ability to produce PCBs with the desired thickness.
What is FR-4 PCB Manufacturing Process
The FR-4 PCB manufacturing process typically involves the following steps:
- Material Preparation: The FR-4 PCB manufacturing process begins with the preparation of the substrate material. This involves cutting the FR-4 sheet to the required size and drilling holes for the components and vias.
- Copper Cladding: The substrate is then coated with a thin layer of copper on both sides. This is typically done using an electroplating process.
- Photoresist Application: A layer of photoresist is then applied to both sides of the substrate. The photoresist is used to create a pattern that defines the location of the copper traces and pads.
- Photolithography: A photomask is placed over the substrate and the board is exposed to UV light. The areas of the photoresist that are exposed to the light will harden, while the areas that are not exposed will remain soft.
- Etching: The board is then placed in an etchant solution, which dissolves the exposed copper. The photoresist is then removed, leaving behind the copper traces and pads.
- Plating: The board is then plated with a thin layer of solder to protect the copper traces and pads and provide a surface for soldering the components.
- Solder Mask Application: A layer of solder mask is applied to both sides of the board to protect the copper traces and pads from oxidation and to prevent solder bridges.
- Silkscreen Printing: A layer of white ink is then applied to the board using a silkscreen printing process. This layer is used to print component labels and other markings on the board.
- Surface Finish: Finally, a surface finish is applied to the board to improve solderability and protect the copper traces and pads from oxidation.
Throughout the FR-4 PCB manufacturing process, quality control measures are implemented to ensure that the board meets the required specifications. These measures include visual inspections, electrical testing, and X-ray inspections to detect any defects or faults in the board.
Performance and Features and Advantages of FR-4 PCB
FR-4 PCB is a popular substrate material widely used in the electronics industry. Its performance, features, and advantages include:
- Good electrical insulation: FR-4 PCB is an excellent electrical insulator, which can effectively prevent short circuits and improve the safety and reliability of electronic devices.
- High mechanical strength: FR-4 PCB has good mechanical properties, such as high strength, toughness, and rigidity, which can provide reliable mechanical support for electronic components and withstand various external stresses.
- Excellent thermal stability: FR-4 PCB has good thermal stability and can maintain its performance even under high-temperature conditions, which is important for many electronic applications.
- Good chemical resistance: FR-4 PCB is highly resistant to most chemicals, such as acids, bases, and solvents, which can ensure the long-term stability and reliability of electronic devices.
- Low water absorption: FR-4 PCB has low water absorption, which can prevent moisture from entering the board and causing damage to the electronic components.
- Easy to process: FR-4 PCB is easy to process and can be designed into various shapes and sizes to meet the needs of different electronic applications.
- Cost-effective: FR-4 PCB is a cost-effective option compared to other high-performance substrates, which makes it an ideal choice for many electronic products.
What are the Applications of FR-4 PCB?
FR-4 PCB is a widely used material in various industries, including consumer electronics, industrial equipment, aerospace, and automotive. Here are some examples of its applications:
- Consumer electronics: FR-4 PCB is commonly used in electronic devices such as computers, smartphones, televisions, and other household appliances due to its high mechanical strength, good electrical performance, and low cost.
- Industrial equipment: FR-4 PCB is suitable for industrial applications due to its high thermal stability, durability, and resistance to harsh environments. It can be used in machinery, control systems, and other industrial equipment.
- Aerospace: FR-4 PCB is used in aerospace applications due to its lightweight, high strength, and resistance to vibration and impact. It can be used in communication systems, navigation systems, and other electronic equipment in spacecraft.
- Automotive: FR-4 PCB is widely used in the automotive industry due to its durability, thermal stability, and resistance to high temperatures and harsh environments. It can be used in various electronic systems in vehicles such as engine control modules, infotainment systems, and safety systems.
Design Considerations for FR-4 PCBs
- Board thickness: FR-4 PCBs are commonly available in thicknesses ranging from 0.4mm to 3.2mm, with 1.6mm being the most commonly used thickness. The thickness of the board impacts the mechanical strength and stability of the PCB. Choosing the right thickness depends on the specific application and requirements. For example, a thicker board may be required for applications that involve high mechanical stress, while a thinner board may be suitable for applications where space is a constraint.
- Trace width and spacing: The minimum trace width and spacing on an FR-4 PCB are determined by the manufacturing capabilities of the PCB manufacturer. Typically, the minimum trace width and spacing for a 1oz copper layer is 0.1mm, while for a 2oz copper layer, it is 0.2mm. Choosing the right trace width and spacing is critical to ensure the desired electrical performance of the circuit. If the trace width is too narrow or the spacing is too small, it can lead to crosstalk, signal integrity issues, and other electrical problems.
- Ground Plane: A ground plane is a large copper plane on one or both sides of the PCB that serves as a reference point for all signals on the board. A solid ground plane is recommended for high-speed circuits to reduce noise and provide EMI shielding.
- Via size and placement: Vias are used to connect different layers of a PCB. The size and placement of vias depend on the specific requirements of the design. If the via size is too small, it can result in high impedance and signal integrity issues. On the other hand, if the via size is too large, it can lead to reduced routing space and increased cost. Proper via placement is also critical to ensure that the vias do not interfere with the signal traces. The diameter of the hole should be at least 0.3mm larger than the lead diameter of the component. The spacing between holes should be at least twice the diameter of the hole.
- Copper thickness: FR-4 PCBs are available with copper thickness ranging from 0.5oz to 3oz. The most common copper weight is 1oz (35μm), but for high current or high-frequency circuits, 2oz or 3oz copper weights may be required. The copper thickness impacts the conductivity and the ability of the PCB to handle high currents. Choosing the right copper thickness depends on the specific requirements of the application. For example, a PCB with high current-carrying capacity may require a thicker copper layer.
- Solder Mask: The solder mask is a layer applied to the surface of the board to protect the copper traces from oxidation and contamination. It also helps to ensure proper soldering during assembly. The solder mask should be applied uniformly, with a thickness of 0.025mm to 0.1mm.
- Silkscreen: The silkscreen layer is used to add markings and labels to the PCB, such as component placement, part numbers, and board revision. The silkscreen layer should be clear and legible, with a minimum font size of 1mm.
Some common errors in FR-4 PCB design include using trace widths and spacings that are too small, placing vias too close to signal traces, and not accounting for the thermal expansion coefficient of the PCB material. To avoid these errors, it is essential to work closely with the PCB manufacturer and adhere to their design guidelines. It is also important to perform thorough testing and validation to ensure the design meets the desired performance requirements.
Get accurate quotes for your FR4 PCB product needs
If you need FR4 PCBs for various projects and product manufacturing processes, we can meet and exceed your demands. We have a world-class standard product facility that enables us to cater to the various services and requests of our customers. To get a precise quote for your FR4 PCB order, you can fill out the request form and we will get back to you by sending an accurate quote based on your needs. If you wish, you can also send us an email at sales@pcbjhy.com. Our phone lines are available at +86 13825274100 for further support.
Why choose us?
When it comes to the leading manufacturer of the best FR4 PCBS, we are simply the best. We have been in the business of manufacturing all types of FR4 PCBs for a wide range of customers. Over the years, we have been able to give our customers the utmost attention and priority when executing their projects. We are a reliable manufacturing company as we have been able to invest both quality and excellence in our business. Our expertise covers the manufacturing, fabricating, and assembly of all types of FR4 PCBs. Our world-class services are offered with the fastest turnaround times without compromising quality. We will constantly supply you with the right quantity and quality of PCBs at the fastest delivery times. Our shipping and logistics solutions ensure that all products are carefully and skillfully assembled to get to each customer quickly and safely.
Explore Our PCB Fabrication Services
Useful Resources
- How PCBs Are Made Step By Step?
- A Comprehensive Guide To Copper Clad Laminate (CCL) Used In PCB Fabrication
- Flexible Copper Clad Laminate (FCCL)
- PCB Prepreg: Definition, Types, Applications, Thickness, And Related Questions Answered
- Complete Guide To PCB Copper Foil
- Resin Coated Copper (RCC)
- What Is Adhesive / Bonding Sheet In Flexible Circuit Board?