At JHYPCB, we specialize in providing a wide range of PCB assembly services to meet the diverse needs of our customers. From prototype builds to high-volume production, we leverage cutting-edge technologies like surface mount technology (SMT) assembly and through-hole technology (THT) assembly to deliver exceptional quality PCB assemblies.
In this article, we’ll provide an in-depth look at SMT assembly versus THT assembly – two of the most common PCB assembly methods used today. We’ll define what each technology is, explore the key differences between them, and discuss when it makes sense to use one over the other. With a better understanding of SMT and THT assembly, you’ll be able to make informed decisions on the best approach for your next PCB project.
SMT assembly and THT assembly each have their own sets of advantages and disadvantages. By the end, you’ll have a clear picture of how these two important PCB assembly technologies complement each other. Optimizing the assembly process ensures efficiency, quality, and reliability – enabling us to meet your prototyping and production needs. Let’s get started!
What is SMT Assembly?
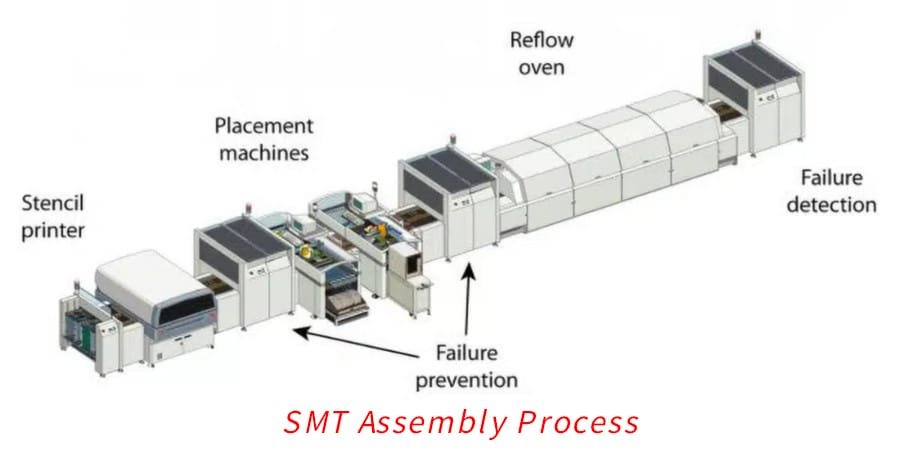
SMT or surface mount technology refers to a PCB assembly process where components are mounted directly onto the surface of a PCB. SMT components are small in size, ranging from chips as tiny as a pinhead to capacitors, resistors, and inductors of various sizes.
The key advantages of SMT components are their compact size, ability to pack more components into a given space, and suitability for automation. This makes SMT ideal for assembling complex, high-density PCBs.
Some common types of SMT components include:
– Chips – Integrated circuits or silicon chips that contain complete electronic circuits. The main component in any electronic device.
– Passive components – Resistors, capacitors, and inductors used to regulate current flow on PCBs. Takes up little space.
– Connectors – Allow connection of PCBs to cables, wires, etc. High-reliability types like the BGA method save real estate.
– LEDs – Light-emitting diodes provide illumination and indicate status. Extremely compact.
The small size and density benefits of SMT components allow for miniaturization of PCB assemblies. Automated pick and place machines precisely mount SMT components onto PCBs very quickly and efficiently. This lends itself well to high-volume production. The quality and precision of SMT assembly also help meet the high-reliability demands of today’s advanced electronics.
What is THT Assembly?
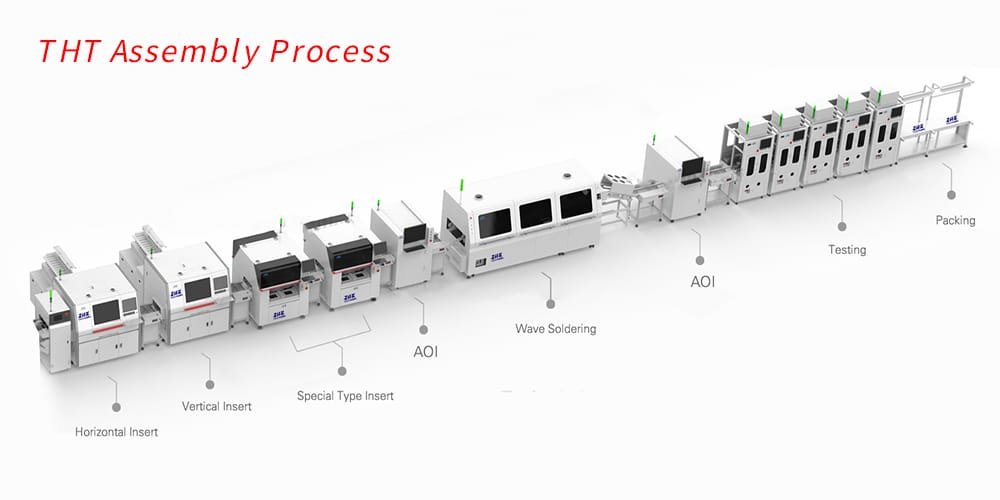
THT, or through-hole technology, is a more traditional method of assembling PCBs that involves inserting component leads into holes drilled in the PCB and soldering them in place from the other side.
Components used in THT assembly include:
– Resistors, capacitors, inductors
– Larger ICs
– Connectors
– Rectifiers, transistors, diodes
– Wire terminals
The defining characteristic of THT components is their leads or pins that fit into the PCB holes. Compared to SMT, THT components are larger and cannot pack densely. However, they have some advantages:
– Easy visual inspection and modification
– Ability to replace individual components
– Less investment in specialized equipment
The through-hole assembly process involves drilling holes, inserting component leads, clinching if required, and wave soldering to make the electrical connections. THT is suitable for simple, low-density PCBs and is widely used in prototyping.
Rework and repairs are easier with THT assembly vs SMT. THT also requires less upfront costs for setting up production lines, making it ideal for lower volume production. For simple analog circuits and power electronics, THT remains an optimal choice.
Key Differences Between SMT and THT
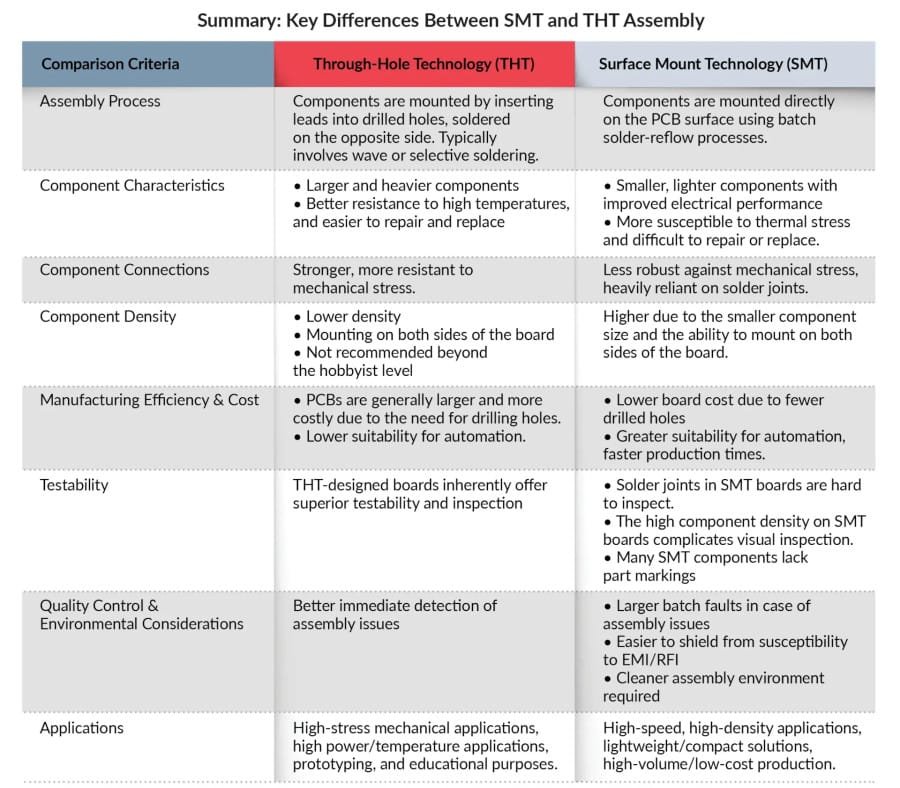
While both SMT and THT are methods to assemble components onto PCBs, there are several key differences between the two technologies:
- Component Size
SMT components are much smaller than their THT counterparts. An SMT resistor may be just 1-2mm instead of 5-7mm for a THT resistor. This compact size allows the fitting more SMT components in the same PCB area. - PCB Density
The small component size enables higher density PCB assemblies with SMT. Components can be placed very close with little waste space on the PCB. In contrast, THT requires adequate spacing between holes to allow drilling and insertion. - Assembly Process
SMT assembly is automated using pick-and-place machines while THT relies more on manual labor for insertion and soldering. SMT has higher upfront costs but faster assembly speed. - Reworkability
It is easier to replace faulty components on THT assemblies where each part can be removed and replaced. Reworking SMT faults requires specialized tools and hot air soldering. - Automation
SMT is highly optimized for automation with specialist equipment for quick high-volume production. THT automation is complex and better suited for prototype builds. - Cost Considerations
SMT has higher startup costs while THT needs less investment in equipment. But for high-volume production, SMT delivers savings from faster assembly and higher yields.
In summary, SMT enables miniaturized and complex PCB assemblies but requires significant expertise and equipment. THT is better for simpler, low-volume builds and offers easier reworkability.
Which Technology Should You Choose?
Deciding between using SMT or THT assembly depends on several factors:
- Manufacturing Volumes
For very high-volume production runs, SMT is preferred for its speed, density, and automation. For moderate or low volumes, THT may suffice and needs lower initial tooling investment. - Design Complexity
Densely packed PCBs with small components are better assembled using SMT. Simpler PCBs can leverage the lower cost of THT assembly. - Space Constraints
If minimizing size is critical, the tiny footprints of SMT components allow compact PCB designs not possible with THT. - Cost Considerations
SMT has higher upfront costs for equipment while THT needs lower initial investment. SMT can drive savings in materials and labor for mass production. - Environmental Conditions
THT withstands vibration and thermal stresses better than SMT joints. But moisture sensitivity is higher for THT components.
For prototyping, THT allows easier debugging and modifications. For streamlined automated production, SMT is preferable. In many cases, a combination of SMT and THT may be optimal. Consulting with assembly experts is recommended to determine the right match for your specific application based on technical and commercial considerations.
SMT and THT at JHYPCB
At JHYPCB, we utilize both SMT and THT assembly technologies to deliver high quality, reliable PCB assemblies tailored to each customer’s requirements.
For prototype builds where quick turnaround, ease of modification, and lower costs are critical, we leverage THT assembly. Our experienced technicians can quickly assemble PCBs with THT components and spot any errors during manual inspection.
For customers needing complex, dense PCB assemblies in medium or high volumes, we utilize advanced SMT lines. High speed pick and place machines precisely mount tiny SMT components, while AOI inspection ensures quality.
JHYPCB is committed to continuous improvement of our SMT capabilities. We invest in the latest equipment, optimize our processes, and train our staff to handle the most complex assembly projects.
Whether your project calls for an urgent prototype build or scheduled mass production, JHYPCB has the SMT and THT assembly expertise and capacity to deliver. Contact our engineers today to discuss your specific PCB assembly needs. We look forward to helping turn your product ideas into reality.
Conclusion
SMT and THT assembly offer two distinct approaches to PCB manufacturing, each with their own pros and cons.
SMT allows for miniaturized components, highly dense PCBs, and automated volume production. But it requires significant upfront investment and specialized skills.
THT is better suited for simpler, low to medium volume PCB assemblies. It offers easier component replacement but lacks the compact size and automation of SMT.
Factors like production volumes, complexity, space constraints, and budget play a role in determining which technology to utilize for a particular product. In many cases, combining both SMT and THT provides the right balance of capabilities.
As an expert PCB assembly manufacturer, JHYPCB is well-versed in both SMT and THT technologies. By leveraging the unique advantages of each, we can deliver optimized solutions tailored for your specific needs.
We hope this overview has helped provide greater insight into SMT vs THT assembly. Please reach out to our team to discuss the best assembly approach for your next PCB project.

















