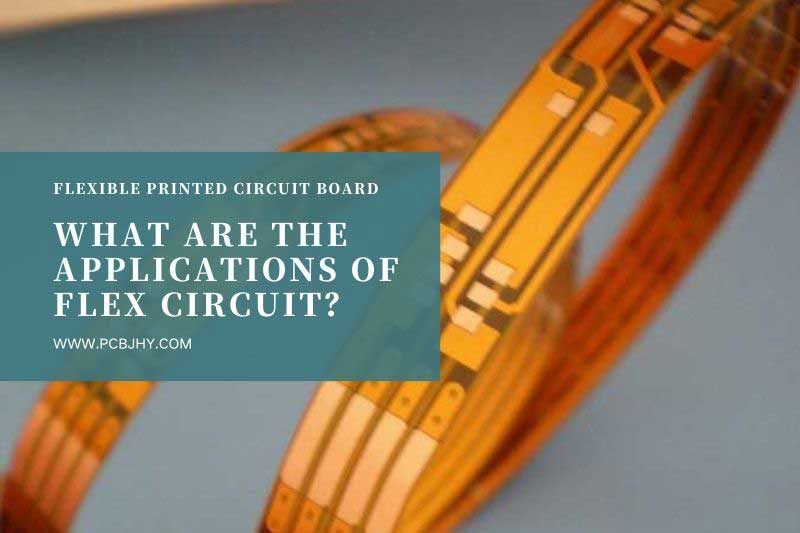
Flexible circuits, also known as flex circuits or flexible printed circuits, have become increasingly important in modern technology. These circuits are made of flexible materials such as polyimide, polyester, or PTFE and can be designed to fit into tight spaces or conform to complex shapes. Flex circuits offer several advantages over traditional rigid circuit boards, including reduced weight and thickness, improved reliability and durability, and the ability to create unique shapes and configurations. These properties make flex circuits ideal for various applications, including consumer electronics, medical devices, automotive and aerospace systems, and many more. In this blog post, we will explore some of the key applications of flex circuits and discuss how they are revolutionizing modern technology. We will examine specific examples of how flex circuits are used in different industries and the advantages they offer over traditional circuit boards. Whether you are a student, engineer, or entrepreneur, this blog post will provide valuable insights into the potential of flex circuits and inspire you to explore new possibilities in your projects or businesses.
Flexible PCB Applications
Consumer Electronics
Consumer electronics have significantly shifted towards flex circuits, also known as flexible printed circuit boards. These circuits are made of flexible materials like polyimide, polyester, or PTFE, offering several advantages over traditional rigid circuit boards. This section will discuss how flex circuits are used in consumer electronics, provide specific examples, and explain their advantages.
- Smartphones, Tablets, and Wearables
Flex circuits are widely used in smartphones, tablets, and wearables. They connect various components such as displays, cameras, and sensors and provide flexible routing of electrical signals. Flex circuits are also used to connect the battery and charging port to the main board. By using flex circuits, these devices can be made thinner, lighter, and more compact.
- Flexible Display Screens
Flexible display screens are one of the most significant applications of flex circuits in consumer electronics. These displays are made using organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs) or liquid crystal displays (LCDs) mounted on flexible plastic substrates. Flex circuits connect these displays to the main board, enabling them to be bent or folded. This technology allows manufacturers to create foldable smartphones, tablets, and wearables, providing new design possibilities and enhancing user experience.
Example: Samsung Galaxy Z Flip
The Samsung Galaxy Z Flip is a smartphone with a foldable display. The display uses a flexible OLED panel and a flexible PCB to connect the display to the main board. The flex circuits allow the display to fold without damaging the electrical connections. By using flex circuits, the Samsung Galaxy Z Flip can be made more durable and innovative.
Example: Fitbit
Fitbit is a popular fitness tracker with a flexible circuit board connecting various components such as sensors, displays, and batteries. The flexible circuit board makes the device lightweight and comfortable to wear.
Advantages of Flex Circuits in Consumer Electronics
Flex circuits offer several advantages over traditional circuit boards in consumer electronics. Firstly, they reduce the size and weight of devices, enabling manufacturers to create smaller and more compact products. Secondly, they improve durability by reducing the risk of damage caused by bending or flexing. Thirdly, they enable new design possibilities, such as creating flexible displays or wearable devices. Lastly, they offer improved reliability and performance, as flex circuits can be designed to have a higher tolerance for temperature, vibration, and other environmental factors.
In conclusion, flex circuits have become a critical component in the development of modern consumer electronics. They offer unique advantages over traditional circuit boards, including reduced size and weight, improved durability, and new design possibilities. As technology advances, we can expect to see even more innovative applications of flex circuits in consumer electronics.

Medical Devices
Flex circuits have become increasingly important in the design of medical devices. Medical devices often require small, lightweight, and flexible components that can be easily integrated into the human body, making flex circuits an ideal solution. In this section, we will discuss the importance of flex circuits in medical devices, provide specific examples, and explain how they improve medical device design.
- Pacemakers
Pacemakers are implantable devices that regulate the heartbeat of individuals with heart conditions. These devices are typically small and require long-lasting power sources. Pacemakers use flexible circuits to connect various components, such as the battery, microprocessor, and electrodes. Flex circuits allow for a smaller and more flexible device, making it easier for the pacemaker to be implanted in the patient.
Example: Medtronic Micra
The Medtronic Micra is a pacemaker only one-tenth the size of traditional pacemakers. The device uses flex circuits to connect the battery, microprocessor, and electrodes. Using flex circuits allows for a smaller, more flexible device implanted directly into the heart, reducing the risk of infection and improving patient comfort.
- Glucose Monitors
Individuals with diabetes use glucose monitors to measure their blood sugar levels. These devices require high accuracy, reliability, and portability. Flex circuits are used in glucose monitors to connect various components, such as the sensor, microprocessor, and display. Flex circuits allow for a smaller, more flexible device that the patient can easily transport.
Example: Abbott FreeStyle Libre
The Abbott FreeStyle Libre is a glucose monitoring system that uses flex circuits to connect the sensor, microprocessor, and display. Using flex circuits allows for a small, lightweight device that the patient can easily wear. The device is also more reliable and accurate due to the flexibility of the circuit board.
- Medical Imaging Equipment
Medical imaging equipment, such as CT scanners and MRI machines, require high accuracy, resolution, and reliability. These devices must also be portable and lightweight for easy transportation between locations. Flex circuits are used in medical imaging equipment to connect various components, such as sensors, processors, and displays. Flex circuits allow for a smaller, more flexible device to be easily transported.
Example: GE Healthcare Optima MR430s
The GE Healthcare Optima MR430s is an MRI machine that uses flex circuits to connect the sensors, processors, and displays. Using flex circuits allows for a smaller and more flexible device that can be easily transported. The device is also more reliable and accurate due to the flexibility of the circuit board.
Advantages of Flex Circuits in Medical Devices
Flex circuits offer several advantages over traditional circuit boards in medical devices. Firstly, they reduce the size and weight of devices, enabling manufacturers to create smaller and more compact products. Secondly, they improve reliability and accuracy by reducing the risk of damage caused by bending or flexing. Thirdly, they offer improved power consumption, as flex circuits can be designed to have a lower power requirement. Lastly, they allow for a more flexible device design, enabling medical device manufacturers to create innovative and more comfortable devices.
In conclusion, flex circuits have become a crucial component in the development of modern medical devices. They offer unique advantages over traditional circuit boards, including reduced size and weight, improved reliability and accuracy, and power consumption. As medical technology advances, we can expect to see even more innovative applications of flex circuits in medical devices.
Automotive and Aerospace Industries
Flex circuits have gained popularity in the automotive and aerospace industries due to their unique advantages, including flexibility, lightweight, and reliability. In this section, we will discuss the applications of flex circuits in these industries, the challenges faced, and how flex circuits can meet these challenges.
- Automotive Industry
The automotive industry has increasingly adopted flex circuits for various applications, such as dashboard displays, engine control modules, and infotainment systems. These applications require flexible, lightweight components that withstand harsh environments, including high temperatures and vibration.
Example: Instrument Cluster Display
The instrument cluster display in modern vehicles requires high-resolution displays that can be easily integrated into the dashboard. Flex circuits connect the various components, including the microcontroller, display, and sensors. Using flex circuits enables a more compact design and improved durability, reducing the risk of failure due to vibration or temperature changes.
- Aerospace Industry
The aerospace industry has used flex circuits for several decades, primarily for satellite communication systems, navigation systems, and avionics applications. These applications require high reliability and durability, as the components are exposed to extreme temperatures, radiation, and vibration.
Example: Satellite Communication System
Satellite communication systems require lightweight and durable components that can withstand the harsh conditions of space. Flex circuits connect the various components, including antennas, solar panels, and power management systems. Using flex circuits enables a more compact and lightweight design, improving the overall efficiency of the satellite.
Challenges and Requirements
Both the automotive and aerospace industries face unique challenges and requirements that must be met by the components used in their products. In the automotive industry, components must withstand high temperatures, vibration, and moisture while being lightweight and compact. In the aerospace industry, components must withstand extreme temperatures, radiation exposure, and vibration while being lightweight and durable.
Advantages of Flex Circuits
Flex circuits offer several advantages in both industries, including reduced weight, improved reliability, and increased design flexibility. The flexibility of the circuits allows them to be integrated into complex designs, reducing the need for additional wiring and connectors. The lightweight nature of the circuits also reduces the overall weight of the vehicle or aircraft, improving fuel efficiency and performance.
In conclusion, flex circuits have become essential in both the automotive and aerospace industries, offering unique advantages over traditional wiring and circuit boards. They can withstand the harsh environments of these industries while reducing weight, improving reliability, and offering increased design flexibility. As these industries continue to advance and innovate, we can expect to see even more applications of flex circuits in the future.
Other Applications
Flex circuits have found applications in a wide range of industries beyond the ones already discussed. This section will briefly mention some of these industries and their applications.
- Military and Defense
The military and defense industries have used flex circuits for various applications, such as communication, navigation, and sensing and control systems. Flex circuits offer unique advantages such as lightweight, compact design, and the ability to withstand harsh environments.
Example: Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs)
UAVs require lightweight and flexible components that can withstand the harsh conditions of their mission environments. Flex circuits connect the various components, including the avionics, sensors, and communication systems. The use of flex circuits enables a more compact and lightweight design, improving the overall efficiency of the UAV.
- Industrial Automation
The industrial automation industry has adopted flex circuits for various applications, such as sensing and control systems, robotics, and flexible lighting. Flex circuits offer unique advantages such as flexibility, compact design, and the ability to operate in tight spaces.
Example: Robotic Arms
Robotic arms require flexible, lightweight components that withstand repetitive motion and tight spaces. Flex circuits connect the various components, including the sensors, motors, and control systems. Using flex circuits enables a more compact and lightweight design, improving the overall efficiency of the robotic arm.
- Smart Home Technology
The smart home technology industry uses flex circuits for various applications, such as flexible lighting and sensing systems. Flex circuits offer unique advantages such as flexibility, compact design, and the ability to conform to various surfaces.
Example: Smart Lighting
Smart lighting requires flexible and lightweight components that can be easily integrated into existing infrastructure. Flex circuits connect the various components, including the sensors, LED arrays, and control systems. Using flex circuits enables a more compact and lightweight design, improving the overall efficiency of the smart lighting system.
In conclusion, flex circuits have found applications in various industries beyond the ones already discussed. They offer unique advantages such as flexibility, lightweight, and compact design, making them ideal for unsuitable applications of traditional wiring and circuit boards. As these industries continue to innovate, we can expect to see even more applications of flex circuits in the future.
Conclusion
In conclusion, flex circuits have become an essential component in modern technology across various industries, including consumer electronics, medical devices, automotive, aerospace, military and defense, industrial automation, and smart home technology. The versatility of flex circuits lies in their ability to offer unique advantages such as flexibility, lightweight, compact design, and improved reliability, making them ideal for applications where traditional wiring and circuit boards are not suitable.
In consumer electronics, we saw how flex circuits are used in smartphones, tablets, and wearables to create flexible display screens, circuit boards, and other components that reduce size and weight, improve durability, and enable new design possibilities. In medical devices, flex circuits are crucial for designing small, lightweight, and flexible components that can improve the accuracy and reliability of devices such as pacemakers, glucose monitors, and medical imaging equipment.
The automotive and aerospace industries have also adopted flex circuits for various applications, such as dashboard displays, engine control modules, and satellite communication systems. The unique challenges of these industries, such as high temperatures, vibration, and radiation exposure, can be met with flex circuits that offer advantages such as reduced weight and improved reliability.
Industries such as military and defense, industrial automation, and smart home technology also use flex circuits for various applications such as sensing and control systems, robotics, and flexible lighting.
As technology continues to evolve, we can expect to see even more applications of flex circuits in the future. Therefore, readers need to consider the potential of flex circuits in their projects or industries. For those interested in learning more about flex circuits and related technologies, numerous resources are available online, such as application notes, technical papers, and tutorials. By leveraging these resources, readers can take advantage of the full potential of flex circuits and drive innovation in their industries.