PCB Electronic Manufacturing Services
What is Hot Air Solder Leveling (HASL)?
Hot Air Solder Leveling (HASL) is a common surface finish method used in PCB manufacturing, where solder and flux are applied to the copper traces and pads on the PCB, and then leveled using hot air to create a smooth and even surface for component placement and soldering.
What is Hot Air Solder Leveling (HASL)?
Hot air solder leveling (HASL) is a common surface finish applied to printed circuit boards to protect copper traces from oxidation and improve solderability.
HASL involves depositing a thin layer of solder alloy onto the bare copper traces of a PCB to coat the traces with a metallic coating. This prevents the copper from being exposed to air and oxidizing over time. The solder alloy coating ensures good solderability – it allows components and wires to be easily soldered onto the board.
The HASL process was first developed in the 1970s as a cost-effective PCB finishing process. In the subsequent decades, it became one of the most widely used finishes thanks to its balance of affordability, ease of implementation, and suitable reliability for many applications.
While new finishes like ENIG and immersion silver have been introduced, HASL continues to be one of the dominant PCB surface treatments today. A large percentage of PCBs manufactured worldwide are still completed with a hot air solder leveling finish.
The main purposes and benefits of the HASL process are:
- Protecting the copper traces from oxidation damage
- Improving solderability for easy component assembly
- Providing a metallic coating for good conductivity
- Cost-effectiveness
- Easy implementation with standard equipment
- Suitable reliability for the majority of applications
With both lead-based and lead-free solder options, HASL remains an optimal choice for many PCB fabrication firms and designers seeking to finish boards in a proven, affordable process.
How HASL Works?
The hot air solder leveling process may sound complicated, but it is actually quite straightforward when broken down step-by-step. Here is a simple explanation of what happens during a typical HASL process:
- Flux Application
The first step is cleaning and preparing the bare copper PCB to receive solder. This involves applying a thin layer of flux onto the copper traces. The flux serves two purposes: removing any oxidation or residues from the copper, and facilitating solder flow and adhesion to the metal surface.
- Preheating
Next, the PCB passes through a preheater unit. This gently warms the board to a temperature between 90-150°C. Preheating expands the copper traces and ensures the flux is fully activated before soldering. It also prevents thermal shock to the board when it contacts molten solder.
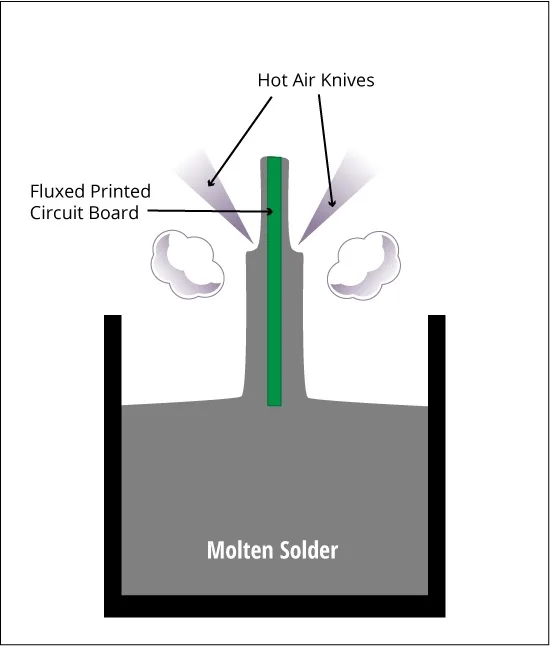
- Molten Solder Wave
The preheated board is transported through a large pumped wave or “fountain” of molten solder alloy. The solder wave coats all exposed copper surfaces with a thin layer of liquid solder as the board passes through. Common alloys used are the tin-lead eutectic 63/37Sn/Pb solder or the lead-free SAC 305 (96.5% tin, 3% silver, 0.5% copper).
- Hot Air Knives
As the board exits the solder wave, hot air knives (also called air knives or leveling knives) blow heated nitrogen or air across the board surface. This serves to flatten and level the liquid solder, eliminating any drips or uneven buildup. The end result is a smooth, uniformly thin solder coating.
- Cooling and Solidification
Finally, the board proceeds into a cooling tunnel. Fans blow cool air to solidify the molten solder into a smooth solid coating on the PCB copper traces. This concludes the HASL process, resulting in a protected board ready for component assembly.
The hot air solder leveling process allows efficient deposition of a thin solder alloy coating in just a few simple steps. This provides ideal oxidation protection and solderability for copper traces in a fast, cost-effective PCB finishing process.
Benefits and Advantages of HASL
There are several important benefits that make hot air solder leveling one of the most popular PCB finishing processes:
- Low Cost
One of the main advantages of HASL is its low cost compared to other finish options. The process requires relatively inexpensive equipment and materials, making it very economically feasible for high-volume PCB production. This cost efficiency has maintained HASL as a leading finish choice.
- Easy Implementation
In addition to low costs, HASL is straightforward to implement in a PCB fabrication line. The basic equipment – solder pump, preheater, leveling knives – is readily available and easy to integrate. There are no complex chemical processes involved as with alternative finishes.
- Good Shelf Life
The solder coating provides excellent oxidation protection for copper traces. Boards finished with HASL have a long shelf life with solderability maintained for at least 12 months when properly stored. This ensures quality over time.
- Suitable Solderability
The solder alloy coating gives good solderability for attaching components and wires. The solder readily melts and flows when heat is applied during assembly. While not as excellent as OSP or ENIG, HASL provides adequate wetting for most applications.
- Widely Applicable
Thanks to its cost-effectiveness and suitable performance, HASL can be used for the majority of PCBs across consumer, industrial, automotive, and other applications. It is a versatile, general-purpose finish option.
- Lead-free Options
As environmental regulations phase out leaded solders, lead-free HASL finishes are now widely available using alloys like SAC305. This allows PCB manufacturers to provide a lead-free surface finish using the same HASL process.
In summary, HASL delivers an optimal balance of affordability, ease of use, adequate reliability, and general applicability to a wide range of PCBs. These advantages make HASL a dependable, high-value option for finishing printed circuit boards.
Downsides and Disadvantages of HASL
While HASL has many benefits, it also has some drawbacks and limitations to consider:
- Not Suitable for Fine Pitch Components
The thin solder coating applied can range from 0.1 to 2 mils in thickness. This may be too thick for boards with ultra-fine pitch components with lead spaces under 4 mils. The increased standoff can cause incomplete joints.
- Thermal Stress on Components
Passing boards through a molten solder wave induces thermal shock stress as components rapidly heat and cool. Delicate components may be damaged or warped under thermal stresses.
- Lower Thermal Conductivity
The solder coating has significantly lower thermal conductivity compared to bare exposed copper. This reduces the thermal dissipation capabilities of the board.
- Oxidation of Exposed Leads
Though the coated traces are protected, component leads and pads are still exposed on the board’s surface. These can oxidize over time prior to assembly which reduces solderability.
- Solder Masks Needed for Lead-free Compatibility
Lead-free solders require higher melting temps. This can cause the HASL finish to re-flow during assembly if not protected by a solder mask over bare copper (SMOBC). This is an additional process step.
While HASL has served reliably for decades, these limitations must be considered when choosing a PCB finish. For more demanding applications, alternative finishes like ENIG or immersion silver may be better suited than HASL.
Comparison to Other PCB Surface Finishes
HASL has both advantages and disadvantages compared to other common PCB finishes like electroless nickel immersion gold (ENIG) and immersion silver. Here is how it compares:
vs. ENIG:
- HASL is lower cost while ENIG involves higher processing costs.
- ENIG provides excellent shelf life exceeding 2 years while HASL shelf life is approximately 12 months.
- ENIG has better thermal conductivity compared to the solder layer in HASL.
- Both provide suitable solderability, but ENIG may have slightly better wetting performance.
- HASL withstands higher temperature processes better than ENIG.
vs. Immersion Silver:
- Immersion silver is more expensive than HASL, but lower cost than ENIG.
- It offers excellent shelf life similar to ENIG.
- Solderability is excellent, potentially better than HASL in some applications.
- Thermal conductivity is not as high as ENIG but better than HASL.
- Silver coating is prone to tarnishing which can reduce solderability over time.
vs. Lead-free HASL
- Solder alloy
- HASL: Typically 63/37 tin/lead or 60/40 tin/lead solder
- Lead-free HASL: Common alloys are SAC305 (Sn/Ag/Cu) or SN100C (Sn/Cu)
- Melting temperature
- HASL: 183°C melting point
- Lead-free HASL: 217-220°C melting point
- Solderability
- Similar solderability performance
- Lead-free may require higher soldering iron temperature
- Shelf life
- Comparable shelf life of around 12 months
- Lead-free finishes may be more prone to tin whiskers
- Environmental
- HASL contains toxic lead
- Lead-free is RoHS compliant and more eco-friendly
- Cost
- Lead-free alloys cost slightly more
- But processing costs are similar overall
- Thermal properties
- Lead-free has slightly better thermal conductivity
- Both have lower thermal performance than bare copper
- Process considerations
- Lead-free compatible solder masks may be required
- Higher melting temp requires parameter adjustments
In general, for less demanding applications where cost is a primary concern, HASL is a good choice. When higher reliability over an extended lifetime is needed, the increased cost of ENIG or immersion silver may be justified.
There is no definitively superior finish. The requirements of the application should determine whether HASL is suitable or if an alternative like ENIG or immersion silver is worth the additional investment.
HASL at JHYPCB
As a leading PCB manufacturer in China, JHYPCB provides professional quality HASL finishing for our customers’ boards.
With over 10 years of experience serving customers globally, we have extensive capabilities in HASL processing for prototyping, low-volume, and high-volume production runs.
We utilize advanced solder leveling equipment to deposit precise and consistent HASL coatings on PCBs. Both lead-based and lead-free SAC305 alloys are available to meet your project needs.
JHYPCB also offers options like HASL finish on selective areas only. This allows combining exposed copper for enhanced thermal dissipation while still protecting other areas prone to oxidation.
Throughout the fabrication process, we perform stringent quality control checks of the HASL coatings including visual inspection, thickness measurements, and solderability testing. This ensures customers receive boards that meet their specifications.
Our engineering team works closely with customers on tailoring the HASL process to optimize quality, cost, and delivery times. We welcome your feedback to continue improving our solutions.
With dedicated domestic support and international sales teams, JHYPCB is ready to fulfill PCB prototyping and production orders with high-quality, affordable HASL finish options. Contact us today to discuss your requirements!