Flexible circuits, also known as flex circuits or flexible printed circuits, are an innovative technology that has revolutionized the electronics industry. They consist of thin, flexible polyimide or polyester film substrates coated with a conductive material layer. The circuits can be bent, twisted, or folded to fit into any shape or space, making them ideal for applications where space is limited or complex geometries are required.
The importance of flexible circuits lies in their ability to reduce the size, weight, and cost of electronic devices while improving their reliability and performance. They also enable the creation of new and innovative designs previously impossible with traditional rigid circuit boards. Flexible circuits are used in various industries, including automotive, aerospace, medical, telecommunications, consumer electronics, etc.
Some common applications of flexible circuits include:
- LCDs
- Mobile devices
- Wearable technology
- Automotive sensors and controls
- Medical devices
- Aerospace and defense systems
- Consumer electronics
- Internet of Things (IoT) devices
As the demand for smaller, lighter, and more efficient electronic devices grows, the importance and applications of flexible circuits will continue to expand.
Single-sided flexible circuits are flexible circuit boards with conductive traces on only one side of the substrate. These circuits are commonly used in applications that require simple and lightweight designs, such as in consumer electronics, automotive sensors, and medical devices.

Single Sided Flexible PCB Stack up
Features:
- Single-sided flexible circuits consist of a thin, flexible substrate made of polyimide or polyester film.
- The conductive traces are printed onto one side of the substrate using etching or screen printing techniques.
- The circuit can be folded, bent, or twisted in any direction, making it ideal for limited-space applications.
Advantages:
- Single-sided flexible circuits are cost-effective and easy to manufacture, requiring fewer materials and processing steps than multi-layer circuits.
- They are lightweight and compact, making them ideal for limited-space applications.
- The flexibility of the circuit allows for a high degree of design freedom, which makes them suitable for a wide range of applications.
Disadvantages:
- Single-sided flexible circuits have limited routing capacity and can only accommodate simple circuit designs.
- They are less durable than multi-layer circuits and more susceptible to bending and flexing damage.
Applications:
- LCDs and touchscreens
- Consumer electronics such as smartphones, tablets, and laptops
- Automotive sensors and controls
- Medical devices such as hearing aids, pacemakers, and medical implants.
In conclusion, single-sided flexible circuits are a popular and versatile type of flexible circuit board that offers many cost, weight, and design flexibility advantages. However, their limited capacity for routing and durability should be considered when choosing the appropriate type of flexible circuit for a specific application.
Double-sided flexible circuits are flexible circuit boards with conductive traces on both sides of the substrate. These circuits are commonly used in applications that require a more complex circuit design but still need the flexibility and lightweight properties of a flexible circuit.

Double Sided Flex PCB Stack up
Features:
- Double-sided flexible circuits consist of a thin, flexible polyimide or polyester film substrate.
- The conductive traces are printed onto both sides of the substrate using etching or screen printing techniques.
- The circuit can be folded, bent, or twisted in any direction, making it ideal for limited-space applications.
Advantages:
- Double-sided flexible circuits offer greater routing flexibility and can accommodate more complex circuit designs than single-sided circuits.
- They are lightweight and compact, making them ideal for limited-space applications.
- The flexibility of the circuit allows for a high degree of design freedom, which makes them suitable for a wide range of applications.
Disadvantages:
- Double-sided flexible circuits are more complex and expensive to manufacture than single-sided circuits.
- They are less durable than multi-layer circuits and more susceptible to bending and flexing damage.
Applications:
- LCDs and touchscreens
- Automotive sensors and controls
- Consumer electronics such as smartphones, tablets, and laptops
- Medical devices such as hearing aids, pacemakers, and medical implants
- Aerospace and defense systems.
In conclusion, double-sided flexible circuits offer a greater degree of routing flexibility and complexity compared to single-sided circuits. Still, they are more expensive to manufacture and less durable than multi-layer circuits. Double-sided flexible circuits are widely used in various industries that require complex circuit designs and a high degree of flexibility, including automotive, aerospace, medical, and consumer electronics.
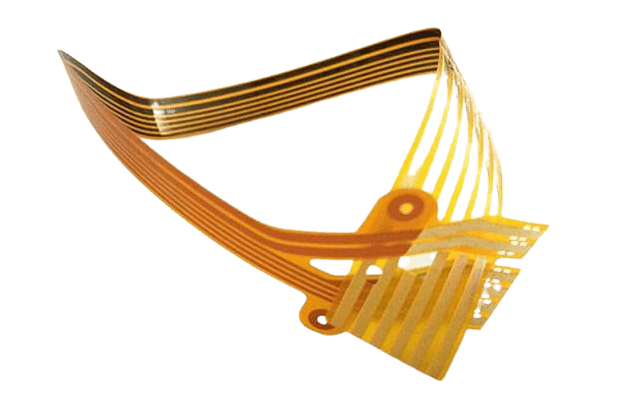

Multi-layer flexible circuits are flexible circuit board that contains multiple layers of conductive traces and insulating layers, similar to traditional rigid printed circuit boards. These circuits are commonly used in applications that require complex circuit designs, high-density routing, and reliability.
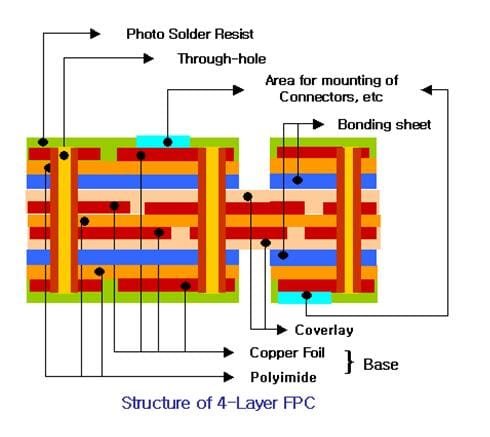
4 Layer Flexile PCB Stack up
Features:
- Multi-layer flexible circuits consist of a thin, flexible polyimide or polyester film substrate.
- The conductive traces are printed onto multiple substrate layers using techniques such as etching or laminating.
- The circuit can be folded, bent, or twisted in any direction, making it ideal for limited-space applications.
Advantages:
- Multi-layer flexible circuits offer greater routing flexibility, density, and complexity than single or double-sided circuits.
- They are more reliable and durable than single or double-sided circuits, making them suitable for high-reliability applications.
- They can reduce a product’s overall size and weight by allowing for more compact designs.
Disadvantages:
- Multi-layer flexible circuits are the most complex and expensive type of flexible circuit to manufacture.
- They may require specialized equipment and expertise for assembly and testing.
Applications:
- Medical devices such as pacemakers and hearing aids
- Aerospace and defense systems
- Consumer electronics such as smartphones, tablets, and laptops
- Industrial controls and automation.
In conclusion, multi-layer flexible circuits are the most complex and expensive type of flexible circuit but offer greater flexibility, density, and complexity than single or double-sided circuits. Multi-layer flexible circuits are widely used in high-reliability applications where space and weight are critical factors, including medical devices, aerospace and defense systems, and consumer electronics.
Rigid-flex circuits are a type of circuit board that combines the benefits of flexible and rigid PCBs, allowing for more complex designs and tighter integration in a single board. The rigid sections provide stability and support for components, while the flexible sections allow for the bending and folding of the board.
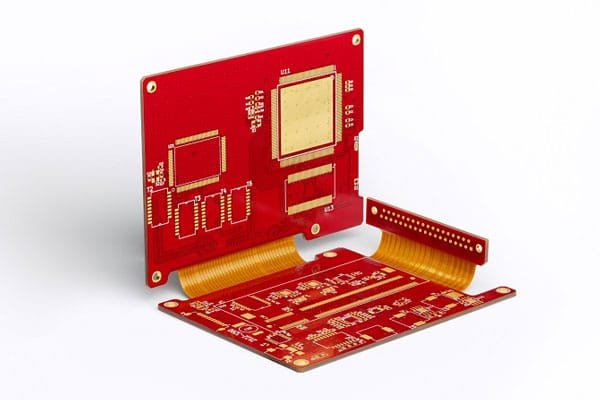

Rigid Flexible PCB
Features:
- Rigid-flex circuits consist of a combination of rigid and flexible substrates that are laminated together.
- The rigid sections support components, while the flexible sections allow for the bending and folding of the board.
- They are designed using a combination of both flexible and rigid PCB design rules.
Advantages:
- Rigid-flex circuits offer more flexibility and versatility in circuit design and integration than traditional rigid or flexible circuits.
- They are more reliable than traditional flexible circuits because they eliminate the need for connectors and reduce the risk of mechanical failure.
- They can reduce board size and weight by combining multiple circuits into one board.
Disadvantages:
- Rigid-flex circuits are more complex and expensive than traditional rigid or flexible circuits.
- They may require specialized design and assembly processes.
Applications:
- Medical devices such as implantable medical devices and diagnostic equipment
- Aerospace and defense systems such as satellites and avionics
- Consumer electronics such as smartphones, tablets, and wearables
- Industrial controls and automation.
In conclusion, rigid-flex circuits offer a combination of the benefits of both rigid and flexible circuits, allowing for more complex designs and tighter integration in a single board. Rigid-flex circuits are widely used in high-reliability applications where space and weight are critical factors, including medical devices, aerospace and defense systems, and consumer electronics.
Sculptured flexible circuits
Sculptured flexible circuits are a type of flexible circuit board designed to have a three-dimensional shape. This type of circuit board is created by bending or twisting a flat substrate to create complex shapes and structures.
Features:
- Sculptured flexible circuits are created by bending or twisting a flat substrate to create complex shapes and structures.
- The substrate is made of polyimide or polyester film, and the circuitry is printed on the surface using traditional PCB manufacturing techniques.
- Sculptured circuits can have varying thicknesses, making them ideal for limited-space applications.
Advantages:
- Sculptured flexible circuits offer greater design flexibility than other types of flexible circuits.
- They can reduce a product’s overall size and weight by allowing for more compact designs.
- They can reduce the need for connectors and wiring, making them more reliable than traditional PCBs.
Disadvantages:
- Sculptured flexible circuits are more complex and difficult to manufacture than traditional ones.
- They may require specialized equipment and expertise for assembly and testing.
Applications:
- Medical devices such as implantable medical devices and diagnostic equipment
- Aerospace and defense systems such as satellites and avionics
- Automotive applications such as dashboard displays and control panels
- Industrial controls and automation.
In conclusion, sculptured flexible circuits are a type of flexible circuit board designed to have a three-dimensional shape. Sculptured circuits offer greater design flexibility than other flexible circuits, allowing for more complex shapes and structures. Sculptured circuits are widely used in high-reliability applications where space and weight are critical factors, including medical devices, aerospace and defense systems, automotive applications, and industrial controls and automation.
Conclusion
In conclusion, flexible circuits are becoming increasingly popular in various industries because they provide a high degree of flexibility and design freedom. Single-sided flexible circuits are a simple and cost-effective option, while double-sided and multi-layer flexible circuits offer increased complexity and functionality. Rigid-flex circuits combine the best of both worlds, allowing for increased reliability and integration in a single board. Finally, sculptured flexible circuits provide even greater design flexibility, allowing for three-dimensional shapes and structures.
Looking to the future, we can expect continued growth and innovation in the field of flexible circuits. Advancements in materials, manufacturing techniques, and design software will enable more complex and efficient designs while reducing costs and lead times. Emerging applications such as wearable technology, the Internet of Things (IoT), and 5G networks will drive demand for flexible circuits, leading to new and exciting developments in the field. Overall, the future looks bright for flexible circuits, and we can expect continued growth and innovation.
Related Reading
- What are the Materials for Flex Circuits?
- Flexible PCBs: Advantages And Disadvantages
- Comprehensive Guide to Manufacturing Flex PCB with Stiffener
- The Ultimate Guide to Flex PCB Stiffener
- Flexible PCB Pricing: Factors, Trends, and Cost-Saving Strategies
- Unlocking the Versatility of Flex Circuit Design: Applications and Benefits
- PET vs. PI: the Differences Between these Materials for Flex PCBs












