What is Multilayer Metal Core PCB?
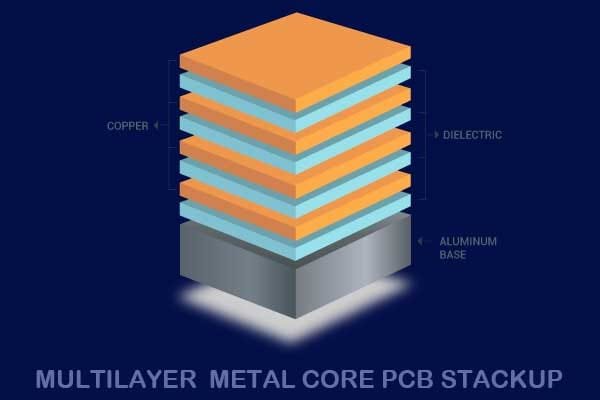
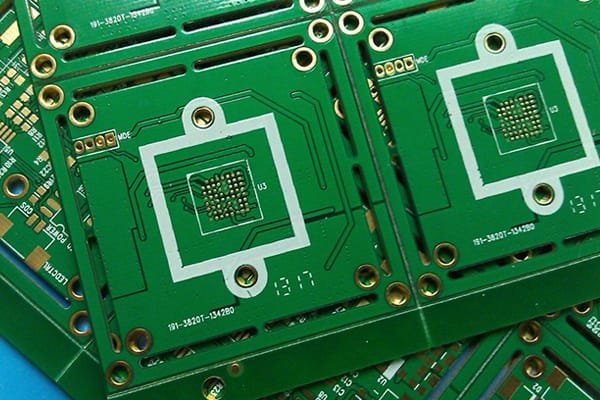
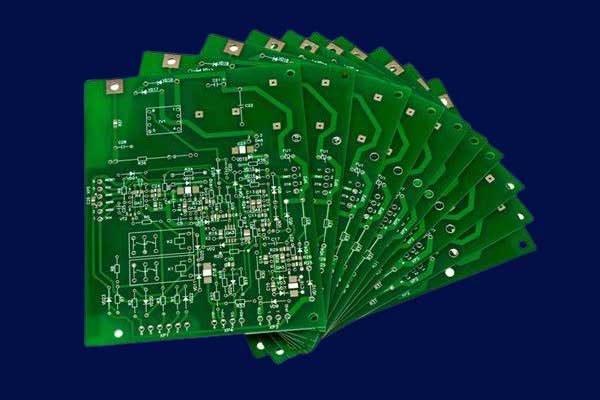
Multilayer metal core PCB (MCPCB) is a type of printed circuit board that consists of multiple layers of conductive traces and insulating materials bonded together with a thermally conductive metal core. The metal core layer provides superior heat dissipation and mechanical stability compared to traditional PCBs, making it an ideal choice for applications that require high power and high thermal dissipation.
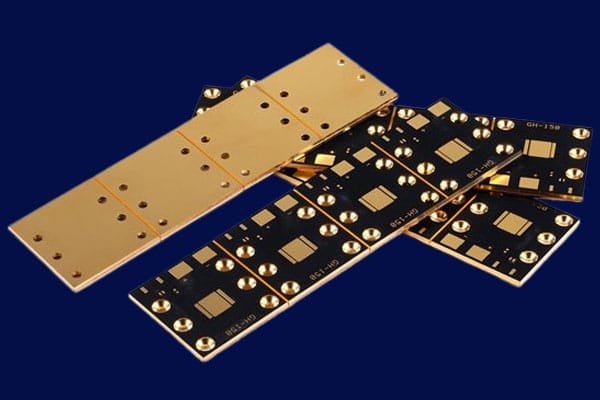
The metal core layer in MCPCBs is typically made of materials with high thermal conductivity, such as aluminum or copper, which allow heat to be dissipated quickly and efficiently from the active components on the PCB. The active layers of the PCB, which contain the conductive traces, are bonded to both sides of the metal core layer using a special bonding process. The insulation layers are then sandwiched between the active layers to create the multilayer structure.
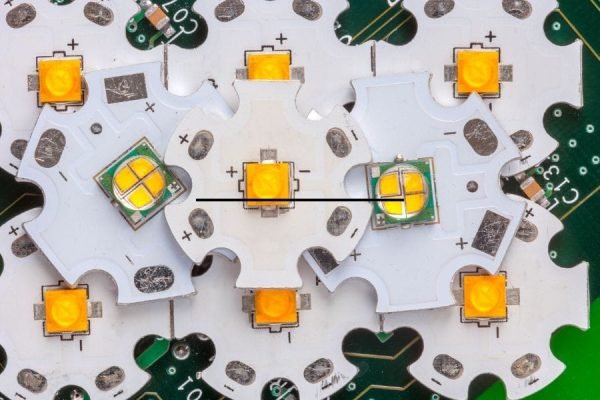
MCPCBs are widely used in various industries such as LED lighting, automotive electronics, and power electronics. LED lighting applications, in particular, have been a driving force behind the increased demand for MCPCBs, as they require efficient heat dissipation to prevent damage to the LEDs and maintain optimal performance. Other applications of MCPCBs include power supplies, motor controllers, and audio amplifiers.
The unique combination of thermal conductivity, mechanical stability, and electrical performance offered by MCPCBs makes them a popular choice for applications that require high power and high thermal dissipation.